What Is Calcined Coke
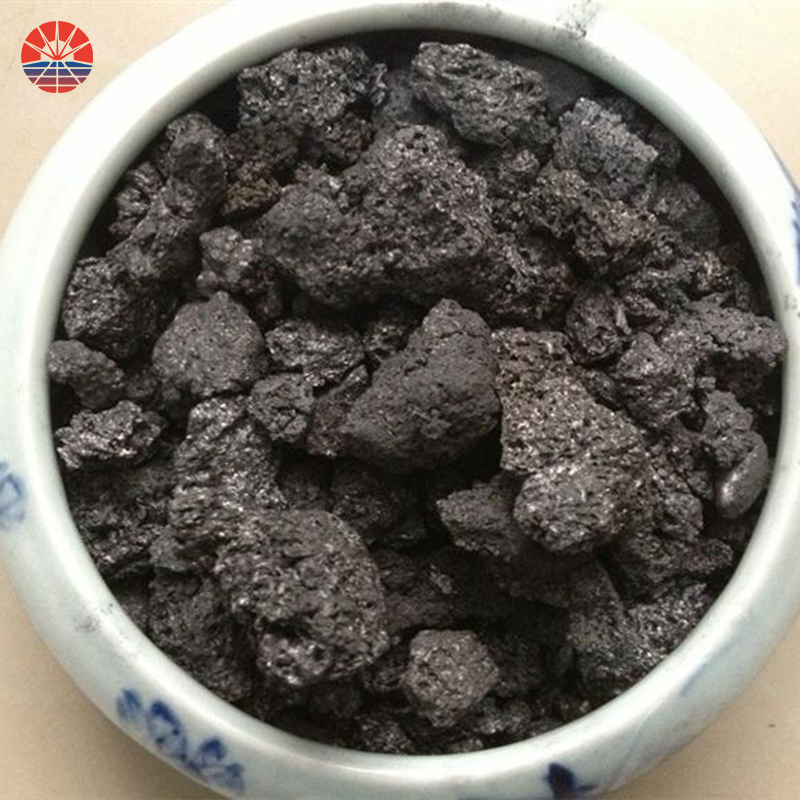
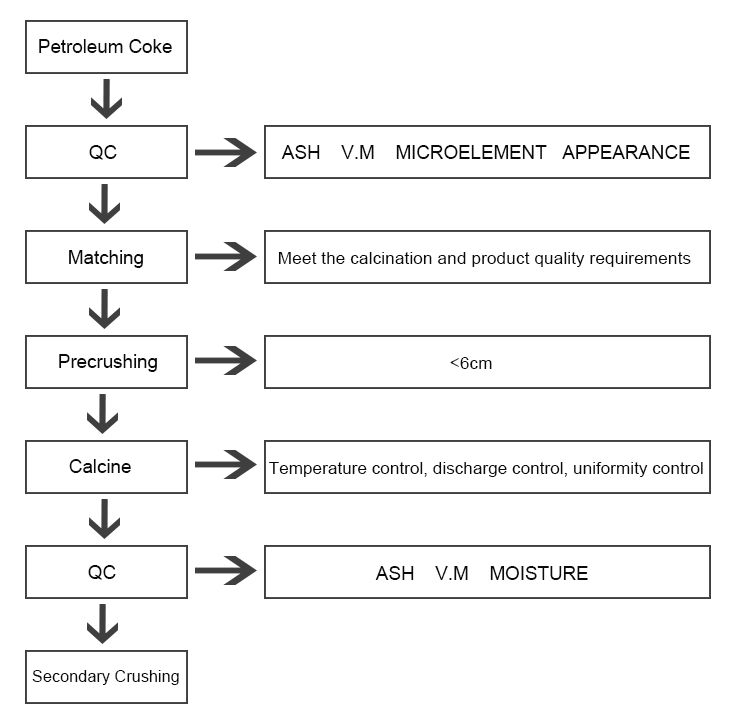
Calcined petroleum coke (CPC) is a high-quality carbon material derived from petroleum residue (also known as green coke). It is produced by heating green coke to remove volatile matter and impurities and to increase its carbon content. The production process of calcined petroleum coke involves several steps, which I will outline below:
Petroleum Coke Production: Petroleum coke is initially produced as a byproduct in the oil refining process. It is obtained from the residue left after the distillation of crude oil. The quality of the green coke, such as its sulfur content and other impurities, can vary depending on the crude oil feedstock and the refining process.
Calcination: The green coke is then subjected to a process called calcination in a rotary kiln. The purpose of calcination is to remove volatile matter, moisture, and other impurities from the green coke. The green coke is fed into the rotary kiln, which is heated to temperatures ranging from 1200°C to 1400°C (2192°F to 2552°F). The heat causes the volatile matter and moisture to evaporate, leaving behind a solid carbon material with a higher carbon content. The calcination process also helps to improve the mechanical strength and electrical conductivity of the coke.
Cooling: After calcination, the calcined coke is discharged from the rotary kiln and enters a cooling system. The cooling process is important to reduce the temperature of the coke and prevent further reactions. Various cooling methods can be employed, such as air quenching or water quenching, depending on the specific requirements of the end use.
Screening and Crushing: The cooled calcined coke is then typically screened to separate it into different size fractions. The desired size fraction depends on the intended application of the coke. After screening, the coke may undergo additional crushing or grinding to achieve the desired particle size distribution.
Packaging and Storage: The final step involves packaging and storage of the calcined petroleum coke. The coke is usually packaged in bags or bulk containers for transportation to customers or storage facilities. Special attention is given to prevent contamination and maintain the quality of the product during handling and storage.
It's worth noting that the production process may vary slightly depending on the specific equipment and technologies used by different manufacturers. Additionally, environmental regulations and quality standards play an important role in determining the process parameters and product specifications for calcined petroleum coke.
CPC role of the negative material
Calcined petroleum coke (CPC) is not typically used as a negative electrode material. In certain applications, however, CPC can be indirectly related to negative electrode materials in the context of lithium-ion batteries.
Negative electrode materials in lithium-ion batteries are commonly made of graphite, specifically a type known as lithium-ion battery graphite. This graphite is typically derived from natural or synthetic graphite sources rather than calcined petroleum coke.
Calcined petroleum coke, on the other hand, finds applications in various industries such as steel, aluminum, and other carbon products. It is primarily used as a carbonaceous material due to its high carbon content, electrical conductivity, and other desirable properties.
In summary, while calcined petroleum coke plays important roles in other fields, it is not typically used as a direct material for negative electrodes in lithium-ion batteries. Graphite materials, including lithium-ion battery graphite, are the commonly preferred choices for the negative electrode in lithium-ion battery systems.