Ferrosilicon Production Process
The production process of ferrosilicon involves the reduction of silica (usually quartz) with iron in an electric arc furnace. Raw materials, including silica and iron, are prepared and charged into the furnace. An electric arc generates intense heat, causing silica to reduce to silicon, and iron to melt and combine with silicon, forming ferrosilicon. The chemical reactions involved are:
1. SiO2 + 2C → Si + 2CO
2. Fe + Si → FeSi
The resultant molten ferrosilicon is cast into molds, cools, and solidifies. It's then crushed or sized into specific forms. Quality control measures are maintained throughout to ensure the desired composition. This alloy is vital in steelmaking as a deoxidizer and alloying agent, enhancing steel quality. Different grades and particle sizes are produced for various applications, making ferrosilicon a crucial material in metallurgical industries.
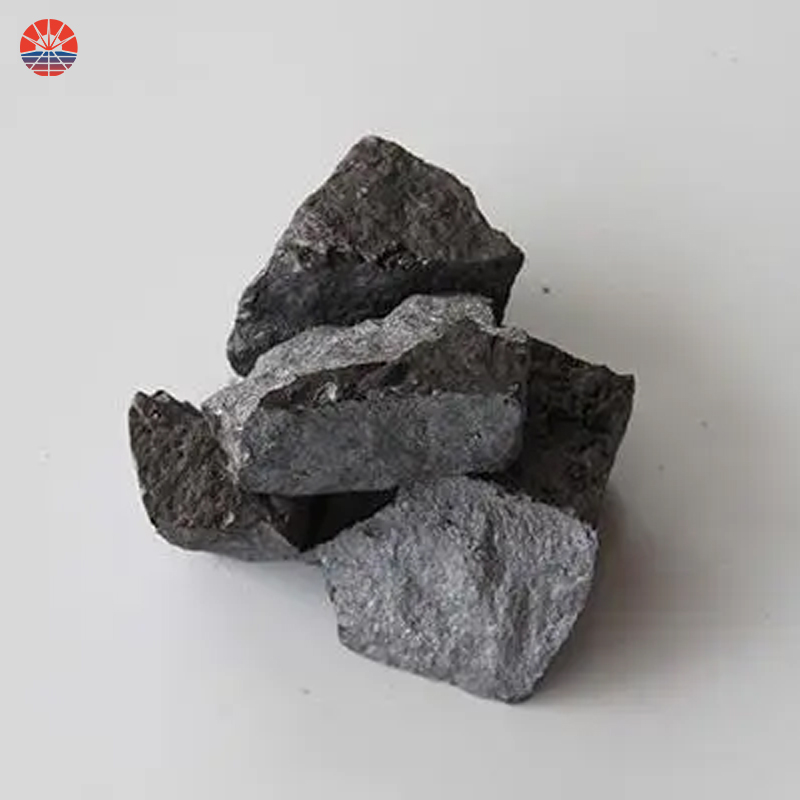
What Is Ferrosilicon
Ferrosilicon is an alloy of iron and silicon, with varying proportions of these two elements depending on the specific application. It is commonly used in the steelmaking and foundry industries to enhance the properties of iron and steel. Here are some key points about ferrosilicon:
1. Composition: Ferrosilicon typically contains around 15% to 90% silicon, with the remaining composition being iron and trace amounts of other elements like carbon, aluminum, and calcium. The exact composition depends on the intended use of the alloy.
2. Deoxidizer and Alloying Agent: Ferrosilicon is primarily used as a deoxidizer and alloying agent in the production of steel and cast iron. It helps remove oxygen and other impurities from molten metal and improves the overall quality and performance of the resulting alloy.
3. Desulfurization: In addition to deoxidation, ferrosilicon is used for desulfurization in the steelmaking process. It helps reduce the sulfur content in steel, which is essential for achieving desired mechanical and chemical properties.
4. Size and Grades: Ferrosilicon is available in various grades and particle sizes, ranging from fine powders to larger granules, to suit different industrial applications. The specific grade and size of ferrosilicon used depend on the requirements of the steel or cast iron being produced.
5. Production Process: Ferrosilicon is typically produced by reducing quartz (silicon dioxide) with coke or charcoal in an electric arc furnace at high temperatures. The result is molten ferrosilicon, which is then solidified and crushed into the desired size.
6. Applications: Besides its primary use in steelmaking, ferrosilicon is also used in the manufacturing of other alloys, such as ferromanganese, ferrochrome, and ferrovanadium. It finds applications in the production of castings, welding electrodes, and as a reductant in various chemical processes.
7. Magnetic Properties: Some grades of ferrosilicon have magnetic properties and are used in the production of magnets, particularly in the electronics and telecommunications industries.
Ferrosilicon plays a critical role in the metallurgical industry, helping to achieve the desired properties and quality of various iron and steel products. Its versatility and ability to enhance the performance of these alloys make it a valuable material in modern manufacturing processes.