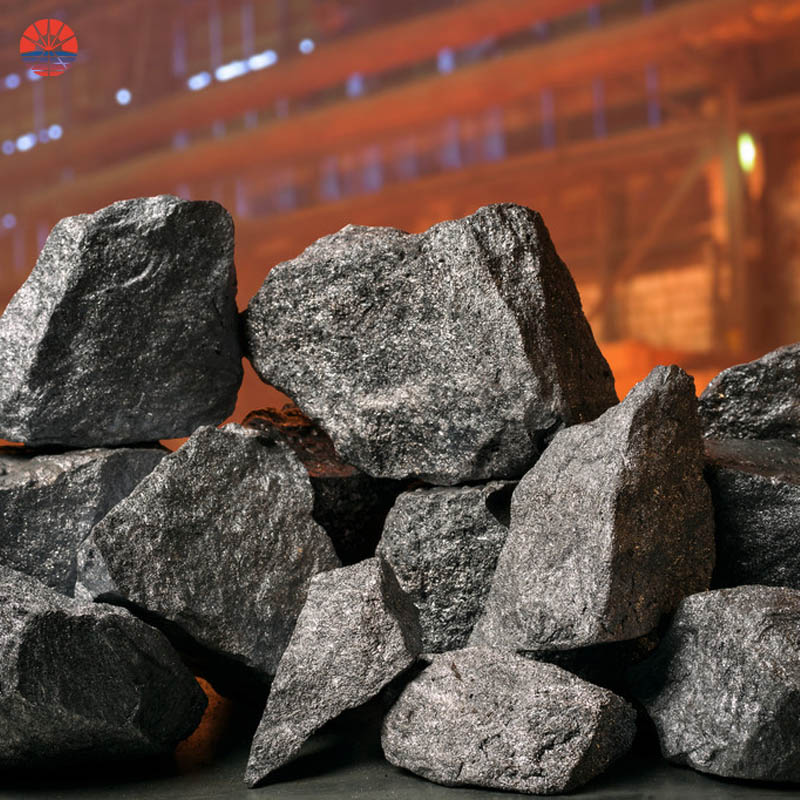
What Is Ferrosilicon Used For
Ferrosilicon is an alloy composed of iron (Fe) and silicon (Si) with varying silicon content, typically ranging from 15% to 90%. It is widely used in various industrial applications due to its unique properties. Here are some common uses of ferrosilicon:
Steel production: The primary application of ferrosilicon is in the production of steel. It is added to iron and carbon in the steelmaking process to improve the final product's properties. Ferrosilicon deoxidizes and reduces the molten steel, removes impurities like sulfur and oxygen, and enhances the steel's strength and quality.
Inoculant in cast iron production: Ferrosilicon is used as an inoculant in the production of cast iron. It helps to control the formation of graphite flakes, which influence the mechanical properties of the cast iron, making it more ductile and less brittle.
Ferroalloy production: Ferrosilicon is a vital component in the production of various other ferroalloys, such as ferrochrome, ferromanganese, and ferrovanadium. These ferroalloys are used to add specific properties to steel and other alloys, depending on the desired end-use.
Dense media separation: In mineral processing, ferrosilicon is used in dense media separation processes to separate valuable minerals from gangue materials. The high density of ferrosilicon makes it an excellent medium for this purpose.
Magnesium production: Ferrosilicon is used in the production of magnesium through the Pidgeon process or the Magnetherm process, where it reduces magnesium oxide (MgO) to magnesium (Mg) using silicon.
Welding and brazing: Ferrosilicon is sometimes used as a deoxidizer and alloying agent in welding and brazing processes, particularly when working with certain types of metals like carbon steel.
Manufacturing of silicon and silicon-based products: Ferrosilicon is a key raw material in the production of silicon and silicon-based materials, such as silicones and silanes, which have numerous applications in industries like electronics, construction, and automotive.
It's essential to note that the silicon content and particle size of ferrosilicon can vary depending on the intended application. Different grades of ferrosilicon are available to meet specific industry requirements.
The Production Process Of Ferrosilicon
The production of ferrosilicon involves the carbothermic reduction of silica (SiO2) and iron sources in a submerged arc furnace. The primary raw materials used in the process are quartz (silica) and iron ore or iron scrap. The production process can be summarized as follows:
Raw materials preparation: Quartz (silica) and iron-bearing materials, such as iron ore, iron pellets, or iron scrap, are crushed and sized to the required specifications. The proper blending of these materials is essential to achieve the desired silicon content in the final ferrosilicon alloy.
Charging the furnace: The prepared mixture of raw materials is loaded into a submerged arc electric furnace. The furnace is typically a large, refractory-lined vessel capable of withstanding high temperatures.
Heating and reduction: Electric current is passed through the electrodes that are submerged in the raw material bed within the furnace. The passage of current generates intense heat and forms an electric arc between the electrodes and the raw materials. This arc provides the necessary heat for the reduction reactions to occur:
SiO2 + 2C → Si + 2CO
Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
In these reactions, carbon (C) acts as the reducing agent, removing oxygen from the silica and iron oxide to produce silicon (Si), iron (Fe), and carbon monoxide (CO).
Alloying and tapping: As the reduction reactions proceed, molten silicon and molten iron are formed. These two components combine to create the ferrosilicon alloy. The alloy composition is controlled by adjusting the proportions of silica and iron in the raw material mix. Once the desired alloy composition is achieved, the molten ferrosilicon is tapped from the furnace and collected in ladles.
Cooling and solidification: The tapped ferrosilicon in the ladles is allowed to cool and solidify. After solidification, the material is broken into smaller pieces, typically referred to as "ingots" or "lumps."
Crushing and sizing: The solidified ferrosilicon is crushed into smaller sizes using crushers, and then it is screened to obtain the desired particle size distribution. Different grades of ferrosilicon may have varying size specifications depending on their intended applications.
Packaging and distribution: The final ferrosilicon product is packaged and transported to various industries that use it for different applications, such as steelmaking, foundries, and other industrial processes.
The production process outlined above is a general description of how ferrosilicon is typically produced. Some variations may exist depending on the specific production plant and the desired grade of ferrosilicon being produced. Additionally, modern production facilities may use advanced technologies to enhance efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and control the alloy's composition more precisely.
Specification
Quality inspection certificate of finished product | |||
Product name | Ferro Silicon | Batch No. | ZC2023-06-13 |
Sampling Site | / | Product specifications | / |
Acceptance date | 2023.06.13 | Report date | 2023.06.14 |
Test items | SH/T 0313-92 | Test results | |
Appearance | This product should be black solid | ||
Si | 75.32 | ||
c | 0.11 | ||
P | 0.03 | ||
s | 0.014 | ||
A1 | 0.77 | ||
Conclusion | Product conforms to specification. | ||